Test and optimise CSF Shunt functionality
Following a shunt implantation, follow-up visits are necessary to evaluate whether unchanged or worsened symptoms can be corrected by shunt adjustment and also to discover any cases of shunt dysfunction requiring surgical shunt revision. Using the Likvor CELDA™️ Instrument in postoperative care can avoid many unnecessary operations and can optimise shunt functionality.
Prevent unneccessary surgery
The CELDA Instrument is the only commercial instrument that accurately can simulate the effect of having a shunt implant and it is also unique in it's capacity to provide data on whether a shunt device needs to be replaced.
Ensure the best possible aftercare
CELDA System makes it easier to follow-up on patients by providing objective and standardised data on the CSF dynamics before and after shunt surgery.
Easy to use
The CELDA™ System contains integrated hardware and software and an easy to use interface for safe and efficient handling. The test protocols are automated and produces standardised reports making the work flow and analysis efficient.

A complete solution for CSF shunt control
Function control
The best way to detect CSF shunt dysfunction
The CELDA Instrument lets you evaluate whether unchanged or worsened symptoms can be corrected by shunt adjustment and also to discover any cases of shunt dysfunction requiring surgical shunt revision.
Optimisation
Optimise the functionality of CSF shunt devices
Even improved patients can benefit with better adjustment of the shunt. In a pre- and postoperative evaluation with the automatic protocol it is easy to determine if a patient’s shunt works as intended.
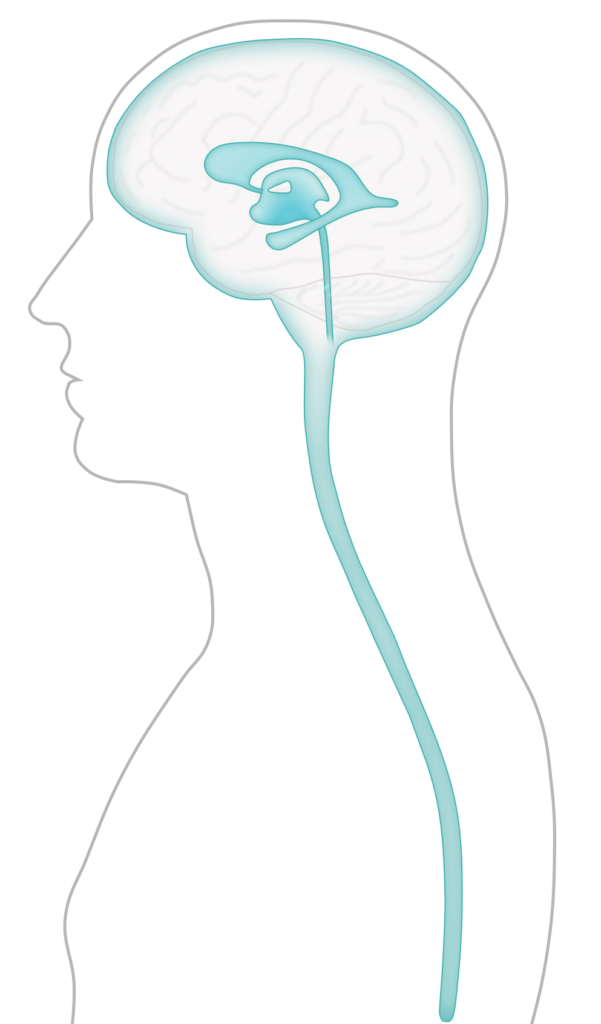
Cerebral Shunt Devices
A cerebral shunt is a medical device commonly used to treat hydrocephalus by relieving pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation.
Shunt systems require frequent monitoring and follow-up. Complications that may occur with shunt systems include:
- mechanical failure
- obstructions
- infections
Malfunctions can lead to serious complications, such as over- or under-draining of CSF. Over-draining occurs when CSF drains from ventricles at a faster rate than it’s produced. This can cause ventricles to collapse, which may lead to headaches or hemorrhage inside the brain. Under-draining allows CSF to accumulate on the brain and can cause symptoms of hydrocephalus to return.